All managers at all levels of every organization perform these functions, but the amount of time a manager spends on each one depends on both the level of management and the specific organization.
A manager wears many hats. Not only is a manager a team leader, but he or she is also a planner, organizer, cheerleader, coach, problem solver, and decision maker — all rolled into one. And these are just a few of a manager's roles.
In addition, managers' schedules are usually jam‐packed. Whether they're busy with employee meetings, unexpected problems, or strategy sessions, managers often find little spare time on their calendars. (And that doesn't even include responding to e‐mail!)
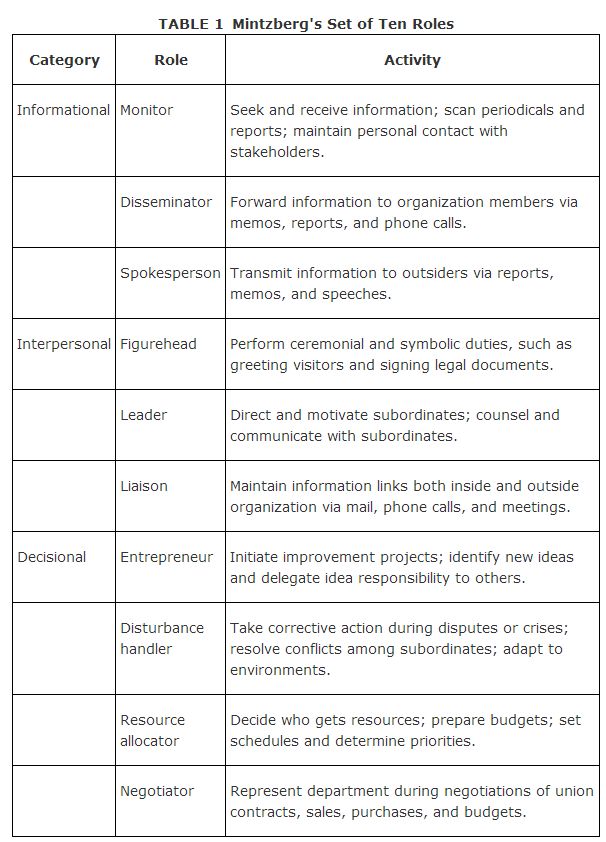
In his classic book, The Nature of Managerial Work, Henry Mintzberg describes a set of ten roles that a manager fills. These roles fall into three categories:
- Interpersonal: This role involves human interaction.
- Informational: This role involves the sharing and analyzing of information.
- Decisional: This role involves decision making.
Table 1 contains a more in‐depth look at each category of roles that help managers carry out all five functions described in the preceding “Functions of Managers” section.
Not everyone can be a manager. Certain skills, or abilities to translate knowledge into action that results in desired performance, are required to help other employees become more productive. These skills fall under the following categories:
- Technical: This skill requires the ability to use a special proficiency or expertise to perform particular tasks. Accountants, engineers, market researchers, and computer scientists, as examples, possess technical skills. Managers acquire these skills initially through formal education and then further develop them through training and job experience. Technical skills are most important at lower levels of management.
- Human: This skill demonstrates the ability to work well in cooperation with others. Human skills emerge in the workplace as a spirit of trust, enthusiasm, and genuine involvement in interpersonal relationships. A manager with good human skills has a high degree of self‐awareness and a capacity to understand or empathize with the feelings of others. Some managers are naturally born with great human skills, while others improve their skills through classes or experience. No matter how human skills are acquired, they're critical for all managers because of the highly interpersonal nature of managerial work.
- Conceptual: This skill calls for the ability to think analytically. Analytical skills enable managers to break down problems into smaller parts, to see the relations among the parts, and to recognize the implications of any one problem for others. As managers assume ever‐higher responsibilities in organizations, they must deal with more ambiguous problems that have long‐term consequences. Again, managers may acquire these skills initially through formal education and then further develop them by training and job experience. The higher the management level, the more important conceptual skills become.
Although all three categories contain skills essential for managers, their relative importance tends to vary by level of managerial responsibility.
Business and management educators are increasingly interested in helping people acquire technical, human, and conceptual skills, and develop specific competencies, or specialized skills, that contribute to high performance in a management job. Following are some of the skills and personal characteristics that the American Assembly of Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB) is urging business schools to help their students develop.
- Leadership — ability to influence others to perform tasks
- Self‐objectivity — ability to evaluate yourself realistically
- Analytic thinking — ability to interpret and explain patterns in information
- Behavioral flexibility — ability to modify personal behavior to react objectively rather than subjectively to accomplish organizational goals
- Oral communication — ability to express ideas clearly in words
- Written communication — ability to express ideas clearly in writing
- Personal impact — ability to create a good impression and instill confidence
- Resistance to stress — ability to perform under stressful conditions
- Tolerance for uncertainty — ability to perform in ambiguous situations