Basic Nouns and Nouns of Quantity
All French nouns have a number (singular or plural) and a gender (masculine or feminine). Singular articles help you to identify the gender of nouns and should be learned with the nouns they modify. Although the gender of some nouns is quite obvious (those that refer to males are masculine, while those that refer to females are feminine), the gender of other nouns can be tricky and must be memorized.
The following list goes into more detail about the number and gender of nouns:
Some noun endings give you a hint as to gender:
- Masculine endings include ‐acle, ‐age, ‐al, ‐eau, ‐et, ‐ier, ‐isme, and ‐ment.
- Feminine endings include ‐ade, ‐ale, ‐ance, ‐ence, ‐ette, ‐ie, ‐ique, ‐oire, ‐sion, and ‐tion.
Some nouns can be either masculine or feminine:
Some nouns can be changed to the feminine by simply adding an ‐e:
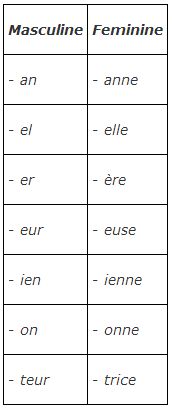
Some masculine nouns (usually referring to professions) have a corresponding feminine ending:
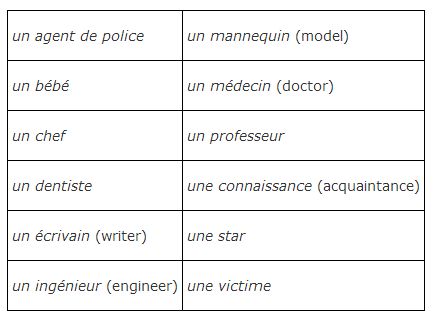
Some words are always masculine or feminine no matter to whom they are referring:
Most French nouns are made plural by adding an unpronounced ‐s to the singular form.
The letters s, x, and z are all used to make plurals in French. If a singular noun ends in any of these letters, its plural form remains unchanged:
Nouns ending in ‐eau add ‐x to form the plural:
- le château → les châteaux
Nouns ending in ‐eu add ‐x to form the plural, except that le pneu (tire) becomes les pneus (tires):
Nouns ending in ‐al change ‐al to ‐aux, except for le bal (which becomes les bals), le festival (which becomes les festivals), and le récital (which becomes les récitals):
Some nouns ending in ‐ou add ‐x to form the plural:
Most compound nouns (nouns made up of two nouns that are usually joined by a hyphen) do not change in the plural. Remember, however, to change their respective articles:
Note the following irregularities:
Some French words are always plural:
French last names do not add an ‐s in the plural:
Nouns that express quantity are followed by the preposition de (d' before a vowel) before the noun that follows. For example:
- Je vais acheter une douzaine d'oeufs. (I'm going to buy a dozen eggs.)
- Donnez‐moi un verre de lait. (Give me a glass of milk.)
High‐frequency nouns of quantity include: