Depreciation is the process of allocating the depreciable cost of a long‐lived asset, except for land which is never depreciated, to expense over the asset's estimated service life. Depreciable cost includes all costs necessary to acquire an asset and make it ready for use minus the asset's expected salvage value, which is the asset's worth at the end of its service life, usually the amount of time the asset is expected to be used in the business. For example, if a truck costs $30,000, has an expected salvage value of $6,000, and has an estimated service life of sixty months, then $24,000 is allocated to expense at a rate of $400 each month ($24,000 ÷ 60 = $400). This method of calculating depreciation expense, called straight‐line depreciation, is the simplest and most widely used method for financial reporting purposes.
Some accountants treat depreciation as a special type of prepaid expense because the adjusting entries have the same effect on the accounts. Accounting records that do not include adjusting entries for depreciation expense overstate assets and net income and understate expenses. Nevertheless, most accountants consider depreciation to be a distinct type of adjustment because of the special account structure used to report depreciation expense on the balance sheet.
Since the original cost of a long‐lived asset should always be readily identifiable, a different type of balance‐sheet account, called a contra‐asset account, is used to record depreciation expense. Increases and normal balances appear on the credit side of a contraasset account. The net book value of long‐lived assets is found by subtracting the contra‐asset account's credit balance from the corresponding asset account's debit balance. Do not confuse book value with market value. Book value is the portion of the asset's cost that has not been written off to expense. Market value is the price some‐one would pay for the asset. These two values are usually different.
Suppose an accountant calculates that a $125,000 piece of equipment depreciates by $1,000 each month. After one month, he makes an adjusting entry to increase (debit) an expense account (depreciation expense–equipment) by $1,000 and to increase (credit) a contra‐asset account (accumulated depreciation–equipment) by $1,000.
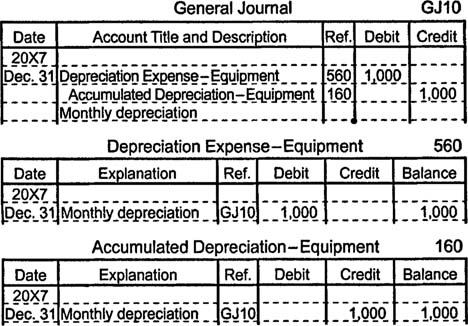
On a balance sheet, the accumulated depreciation account's balance is subtracted from the equipment account's balance to show the equipment's net book value.
ACME Manufacturing Partial Balance Sheet December 31, 20X7
|
Property, Plant, and Equipment
|
|
|
|
Equipment
|
125,000
|
|
|
Less: Accumulated Depreciation
|
(1,000)
|
124,000
|