Introduction to Incremental Analysis
Managerial decisions are choices made based on financial and nonfinancial information. Typically, financial information serves as the first hurdle in identifying a possible course of action as an alternative. If the financial hurdle is met, then management must consider the impact of the alternative on the environment, the company's employees, its image, the community, its partners or alliances, and so on before making a final decision.
Incremental analysis, sometimes called marginal or differential analysis, is used to analyze the financial information needed for decision making. It identifies the relevant revenues and/or costs of each alternative and the expected impact of the alternative on future income.
To illustrate the concept, think about the decision to lease or buy a car. Leasing involves a regular payment and the return of the vehicle at the end of the lease unless a one‐time payment is made. This arrangement means the car does not legally belong to the person leasing it. To buy a car requires payment of the purchase price. The payment may be made in cash or by signing a note payable for the amount owed. If you were to prepare financial statements under each alternative, they would look very different. An operating lease for a car with payments of $300 per month would result in the annual cost of the lease, $3,600, being reported as an expense on the income statement. The purchase of a car results in an asset — and a liability, if a note was signed — being recorded on the company's balance sheet.
Another example is the choice between alternatives A and B, given the following relevant revenues and expenses:
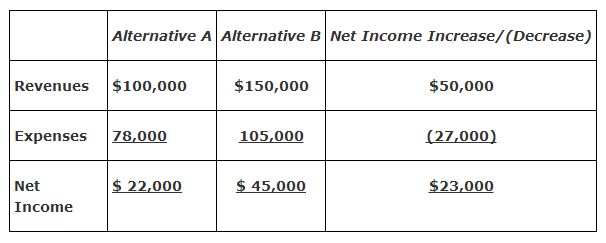
This example shows alternative B generates $23,000 more net income than alternative A. Management must now consider the nonfinancial information to determine whether alternative B should be accepted.
Several concepts are incorporated into incremental analysis and need to be defined before discussing some specific applications of incremental analysis.
- Relevant cost. Those revenues and costs that differ among alternatives, as opposed to revenues and costs that stay the same, which are ignored when analyzing alternatives. Note: Some texts refer to the revenues that change as relevant benefits.
- Sunk cost. A cost that has already been incurred and, therefore, has no impact on future decisions because the cost will not change or go away in the future. The book value of a previously purchased and currently owned asset will not change whether or not a new asset is purchased to replace it.
- Opportunity cost. A potential benefit that is lost when a company chooses another alternative.
|
|