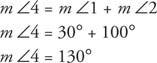Exterior Angle of a Triangle
An exterior angle of a triangle is formed when one side of a triangle is extended. The nonstraight angle (the one that is not just the extension of the side) outside the triangle, but adjacent to an interior angle, is an exterior angle of the triangle (Figure 1 ).
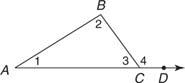
Figure 1 Exterior angle of a triangle.
In Figure 1, ∠ BCD is an exterior angle of Δ ABC.
Because m ∠1 + m ∠2 + m ∠3 = 180°, and m ∠3 + m ∠4 = 180°, you can prove that m ∠4 = m ∠1 + m ∠2. This is stated as a theorem.
Theorem 26: An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two remote (nonadjacent) interior angles.
Example 1: In Figure 1, if m ∠1 = 30° and m ∠2 = 100°, find m ∠4.
Because ∠4 is an exterior angle of the triangle,